For years, collagen has been a beauty buzzword. Although collagen's skin-plumping abilities are touted, it keeps a body together in ways that are more than skin-deep.
It’s a promising treatment that helps bones and joints heal in sports injuries and osteoarthritis. Other ways collagen may benefit health is by enhancing immunity and helping to repair a leaky gut, according to some functional medicine doctors.
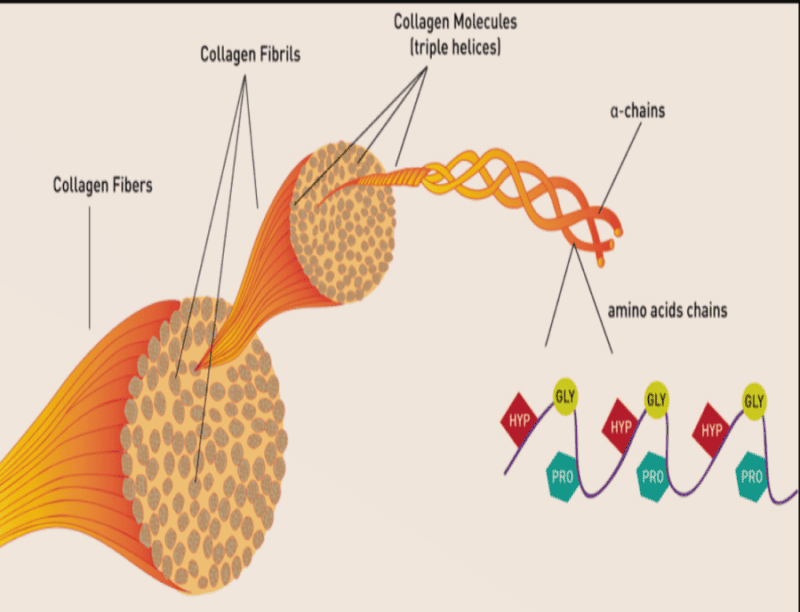
AMINO ACIDS AND COLLAGEN
Would you like to save this recipe or article?
You won't get spam from me, I promise!
Collagen is a tightly coiled protein with a triple helix structure most often consisting of the amino acids glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline.
Other common amino acids in collagen are lysine, hydroxylysine, and valine – the latter is an essential amino acid (meaning the body cannot produce it) in gelatin, a less hydrolyzed (or broken apart) form of collagen. Lysine is also one of the nine essential amino acids. It’s worth noting that collagen does not contain all of these. It lacks tryptophan.
Every tissue in our bodies contains some form of collagen, and there are many types. Bones, teeth, tendons, ligaments, fascia, blood vessels – even eyeballs contain collagen. This structural protein makes up 25 to 35% of all the proteins in our bodies. It’s a largish molecule that is unlikely to be taken up by skin through the application of a cream.
BEAUTY BENEFITS
More likely, it bestows wrinkle-abating and hydrating effects for skin if you eat it – either as food or as a supplement.
A recent double-blind placebo-controlled study with about 60 women aged 40 to 60 years old who had crow’s feet around their eyes found collagen increased skin elasticity, hydration, and smoothed wrinkling.
To ensure that the results seen in the study were from treatment with collagen supplements, the women did not use topical retinoid creams or lasers for their skin.
The researchers used collagen hydrolysates for the study as this type of collagen peptide is thought to be easily absorbed. The women in the study took about 1 gram/day. Other researchers have recommended up to 5 grams/day.
You need to be cautious if you want to try collagen as a dermal filler and have a skin patch test before having it injected.
Collagen fillers are derived from bovine sources, and although you may not think you are allergic, it’s important to test and be sure that the product will not cause redness and swelling. 🐮
(Many people are allergic to bovine collagen, which is one of many reasons that hyaluronic acid and other fillers are more popular. They are unlikely to provoke an angry reaction after being injected.)
Some people have noticed that taking a daily dose of collagen or gelatin also improves hair, skin, and nails.
Kevin Koch, a stylist at Lisa Bennett Salon in Dallas, said that some of his clients have noticed better hair texture and less brittle nails while using collagen supplements.
Joint 911
A 2017 review on collagen and osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis concluded that collagen was helpful with pain in osteoarthritis, but not in rheumatoid arthritis.
A 2018 review of studies on collagen and joint healing showed that collagen was better than glucosamine and chondroitin against pain, stiffness, and function. Study participants using collagen also had improved knee extension and a longer amount of active time before they felt joint pain.
The research in this review was not done with hydrolyzed collagen (peptides). The collagen in this study was undenatured type II collagen available as 40 mg capsules, taken once a day.
Type II collagen is the kind found in articular (the kind found in joints) cartilage.
The other important point this review mentioned is that when it comes to injuries, collagen speeds up healing early in the process, but long-term outcomes were not improved by collagen supplementation.
Recent research by Baar (2017) shows that a 15 mg gelatin capsule taken 30 to 60 minutes prior to therapy exercise can augment collagen production.
Given that gelatin is simply another form of collagen and contains most of the same amino acids, this makes sense.
BONE BUILDING
Just as collagen speeds recovery in tendons and ligaments, healing of broken bones is also accelerated. Beyond this, collagen may improve bone mineral density in older people.
One recent study conducted with post-menopausal women – a group at higher risk of fracture – found that collagen peptide doses of 5 grams/day were able to increase bone mineral density.
These women had already lost significant bone mass before volunteering for the study. (They also were not using other medications for bone loss.)
IMMUNITY
The arthritis review’s authors (2018) mention that type II collagen makes up most of the collagen in cartilage and note that osteoarthritic cartilage contains antibodies that are anti-type II.
They say that this means pathways in your immune system are involved in the development of osteoarthritis.
The redness, swelling, and pain of inflammation can also signal autoimmunity in which the body attacks its own tissues. The undenatured type II collagen reduced this overresponse by its effect on the gut.
Half or more of your immune system resides in the digestive tract and is known as Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (or GALT).
If you have digestive problems, the immune system can falter and you can develop any number of conditions including arthritis or diabetes.
Leaky gut, a condition in which bacteria and toxins leak through the intestinal wall, is associated with autoimmunity.
Some functional practitioners see leaky gut as related to damaged GALT and promote the use of collagen as an anti-inflammatory to boost GALT integrity and soothe leaky gut.
NOTE: Mainstream medical doctors do not recognize leaky gut as a medical condition.
TWO MICRONUTRIENTS THAT HELP COLLAGEN WORK ITS MAGIC
- Vitamin C is key for getting collagen to have an effect on the body. It facilitates enzymatic reactions that help procollagen march down the biochemical pathway that turns it into collagen.
When you have scurvy from vitamin C deficiency, you experience muscle weakness and little red freckling from the breakage of weak capillaries. This is because your body can’t properly knit together collagen without the help of vitamin C.
The other assist from vitamin C has to do with inflammation caused by free radicals.
This inflammation can cause both the visual effects of aging, aka the breakdown of the skin resulting in laxness and wrinkles, and the pain and loss of articular cartilage associated with osteoarthritis.
Vitamin C’s antioxidant prowess in mopping up free radicals, also known as reactive oxygen species (ROS), is well documented.
This does not mean you should load up on mega-doses. Using large amounts of vitamin C, doses of 1,000 mg, for example, could inhibit healing in muscles and joints.
For this purpose, doses should probably not exceed 250 to 500 mg. The latter is also plenty for beauty benefits. Bear in mind, that smokers will require slightly more since smoking inhibits blood flow to the skin and causes oxidative stress.
Fruit and vegetables with vitamin C:
- Citrus fruits and juices
- Potatoes
- Bell peppers
- Kiwi fruit
- Cantaloupe
- Papaya
- Copper is the other essential micronutrient/trace mineral that helps collagen work its magic. Supplements of copper are rarely necessary and can interfere with the absorption of other important micronutrient metals like iron and zinc.
Foods with copper
- Sesame seeds
- Cocoa powder
- Shellfish
- Cashews and almonds
- Dried fruits
- Whole grains
COLLAGEN: THE BOTTOM LINE
Although supplements may seem like a simple way to get collagen, they can be costly. Many nourishing foods, described below, are good sources. When you’re thinking of supplements, always remember, FOOD FIRST!
Most collagen comes from the skin, organs, bones, and hooves of animals, so the best sources of collagen are animal foods.
Some collagen supplements come from fish (marine collagen), and soy foods contain glycine and proline, the two most important amino acids in collagen.
Collagen is a frequent therapy for aging skin, for healthy joints, and for immunity.
Other uses include:
- gut function
- increasing muscle mass,
- weight loss
- reduction of cellulite
- wound healing
Collagen supplements and foods do not appear to have bad side effects although some people have reported bloating and a feeling of fullness.
Also, although collagen has lots of research behind it, few of the studies have human subjects. Much of what we know comes from research conducted on animals. 🐀
The problem with this research is that many animals can endogenously create their own vitamin C (see discussion of this vitamin above).
Humans must eat vitamin C as food or supplements. This can make conclusions drawn from animal research less relevant and useful.
| The most common types of collagen: Types I-V |
|---|
| Type I: For strong hair, nails, skin, organs, bones, and ligaments. Excellent for skin elasticity. One study suggests the use of marine collagen for beauty. Type II: For articular cartilage in your joints and for immunity. Collagen made from chickens may be best for this purpose. Type III: Also good for hair and skin, but especially beneficial for blood vessels and cardiovascular health. It is sourced from cows (bovine collagen). Type IV: Also seen in skin, it is a unique part of the cell membrane with many functions including linking to connective tissue. It does not form the usual helical shape of collagen. Allergenic markers in this collagen have been linked to rheumatic disease. Type V: Sourced from the membranes of eggshells, this type of collagen is found in the placenta and the cornea. |
All types of collagen will stimulate your body to create collagen. Look for easily absorbed hydrolyzed peptides if you are buying a supplement. 👀 |
Here's an easy recipe that is a two-fer. Chicken for dinner and bone broth--full of collagen--for soup the next day!

Instant Pot Whole Chicken with Rosemary
Equipment
- Instant pot trivet
- Measuring cup
- Knife
- Cutting board for meat with shallow groove around the edges to catch the juices
Ingredients
- 1 whole chicken about 3 to 4 pounds
- Salt and pepper
- 1 lemon quartered
- A generous fistful of rosemary branches
- ½ cup water
- 🌿🌿🌿🌿
Instructions
- Remove any giblets and neck bone from chicken. (Save them for stock and/or gravy, if you wish.)
- Season the cavity and exterior of bird with salt and pepper.
- Place two lemon quarters in the cavity.
- Put the trivet in the bottom of the instant pot and pour the water over it.
- Place the chicken on top and cover with the rosemary. (Don't worry if some of the herb falls to the side.)
- Put the lid on and seal the vent. Cook on high pressure for 35 minutes.
- Quick release the steam/pressure through the vent, being careful not to burn yourself.
- Remove the lid and take the bird out onto a meat board to carve.
Notes
Nutrition
Copyright © 2020 Jani Hall Leuschel







jani
Some of the functional medicine doctors recommend adding glutamine to the collagen and other substances to optimize its effect on the gut. I would be careful about taking a large dose of collagen peptides (hydrolyzed product) for gut healing as one scoop (equal to 10 g of collagen and 9 g of protein) may cause bloating and will definitely nix any feelings of hunger, depending on body size.
Your body's production of collagen slows dramatically with age, so supplementation with gelatin, capsules, or peptides makes sense. Of course, foods rich in collagen, such as soups and stews tend to be very satisfying. Theoretically, vegetarian collagen should be almost as good for stimulating bone health as it contains most of the same amino acids. My next post will examine soy-based foods and other sources of collagen for vegetarians.
Thanks for your comment!
kdk4503
Had no idea the huge benefits of collagen--always thought of it as a beauty aid! Interesting that it can be of real use in the gut which often causes so much trouble for older folks (like myself!) Also interesting that it improves bone density--but I guess that type has to come from our four-legged friends! Thanks, also, for mentioning functional doctors; I think it's a promising fronteir in medicine.
jani
Hi Bill,
Thanks for sharing your thoughts and for the thumbs up on my photos! I'm glad you were able to use this info. Collagen is terrific for joints, and it's encouraging to hear that you stay active because physical activity is actually the best tool to keep your joints healthy. That said, wear and tear happens to all of us, especially those who have a regular program of exercise.
It does take longer to recover when your body has few more miles on it. (I know this from personal experience!) Sleep and diet are the two major keys to recovery, but extras like collagen, whey protein, and B-complex vitamin can also give you a helping hand. It's also good to evaluate your program. If it consistently makes you sore and hurts your joints, maybe tweaking and changing it up a bit will help, too.
Cheers! Good to hear from you!
Bill
Thanks for the new, immediately useful information on collagen: A relatively easy dose, 40mg, can help us, um, maturing types with joint healing. As an active senior, quicker recovery tools are very helpful to continuing my enjoyment of physical activity. PS Great photos - they show up much better than most sites!